How Do Brita Filters Work?
Brita is a popular water filter brand offering a variety of filtration systems for home and travel. But what exactly is the science behind their filters? How does a Brita pitcher filter work to provide clean, fresh-tasting water?
Brita water filter pitchers use several different methods to filter tap water. Each BPA-free housing of standard filters contains coconuts-based activated carbon granules and ion exchange resin. The carbon filter removes the chlorine taste and odor.

The ion exchange resin, on the other hand, removes the heavy metals, cadmium, copper, and zinc.
Brita Elite filters remove more contaminants and last longer than standard filters thanks to their pleated filter technology and industry-secret carbon-based filter. Aside from heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, Brita Elite filters also remove some types of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), pesticides, pharmaceutical residues, asbestos, and sediments.
Brita’s Stream filters use an activated carbon filter to remove contaminants such as 1,2,4 Trichlorobenzene- a type of volatile organic compound (VOC) and Class VI particulates that are more than 50 micrometers. It also reduces chlorine taste and odor.
Brita’s advanced filtration technology makes it easy to get cleaner-tasting drinking water right from your tap at home – no extra equipment or installation is needed!
Do Brita Filters Remove Lead?
The answer depends on the type of Brita water filter as some Brita filters remove lead from the drinking water but some do not.
Brita Filters That Remove Lead
Brita filters are a popular household item used to reduce contaminants in drinking water. The following Brita filters remove lead from the drinking water:
Elite Filters (Longlast)
Brita Elite Filter or Longlast Filter is designed to eliminate lead from water. Each carbon-based Brita Longlast filter works like a magnet attracting lead and other impurities. They are then stuck in the filter, removing them from the water.
These water filters are tested and certified to NSF/ANSI 53 to reduce two forms of lead per the requirements of the standards. They can filter up to 99.5% of lead from water at pH 6.5 and 99.6% from water at pH 8.5.
Faucet Filters
A Carbon-based Brita Faucet Filter is also a great way to help reduce lead in your drinking water. It is also certified to NSF/ANSI 53 and can remove up to 99.3% of lead from source water.

Brita Water Filters That Do Not Remove Lead
Standard Filters
Brita Standard Filters are widely used to reduce contaminants in drinking water, but unfortunately, they do not remove lead properly. It is therefore important to understand the limitations of Brita Standard Filters when providing safe drinking water for your family. You can check out further details about Brita Standard or Longlast filters in this Brita review.
Stream Filters
Brita Stream Filters are a popular choice for many people looking to reduce unwanted contaminants in their drinking water. However, potential consumers should know that this filtration system does not remove lead from water.
Bottle Filters
Brita Bottle Filters are also popular for people wanting filtered water wherever they go. While Brita bottle filters remove sediments, chlorine taste, and odor, but they do not remove lead from water coming through lead pipes.

How Lead Contaminates Water?
Lead contamination in water is a serious matter that needs to be addressed. Lead, a toxic metal, has been linked to numerous health risks when present in drinking water.
Water pipes, fittings, and fixtures containing lead are now banned in the US. However, most water supplies are exposed to old corroded pipes and fittings that have lead or those that are joined with lead solder, as they are still used today. This is the number one source of lead in water.
What about well water? Even well water can be contaminated with lead as it can enter groundwater from plumbing, gasoline, and industries like the automobile industry that use lead in storage batteries and radiators.
Whether using city or well water, lead can find its way into our homes and cause serious health issues.
How to Test Your Tap Water for Lead?
Testing your tap water for lead is an important step in ensuring that you and your family are being provided with safe drinking water. Lead can enter the water supply through old pipes, fixtures, and fittings, which makes it important to make sure your home does not have elevated levels of lead.
It’s a fairly simple process to test for the lead but requires you to collect samples from various taps in your home.
Water Test Kit
To begin testing for lead in your water, purchase a water test kit from a local store or online retailer.
The kit will generally come with a test strip, which you place in a water sample and wait for the results. These kits can be purchased individually or as part of a larger kit that also includes testing for other contaminants such as bacteria, iron, and more.
These strips contain chemicals that react when exposed to certain water contaminants. Users then consult the corresponding color chart to check the presence of the contaminants.
Remember that test strips only indicate the presence or absence of contaminants in your water. They do not tell you an accurate reading of the contaminants in the sample.

Laboratory Testing
Laboratory testing offers a more accurate method of your water’s lead content. It involves collecting a tap water sample from your home and sending it to a certified laboratory for testing.
The lab will then analyze the sample and provide results about the amount of lead present in the sample and whether or not it exceeds any recommended safety thresholds established by governmental agencies such as EPA (Environmental Protection Agency).
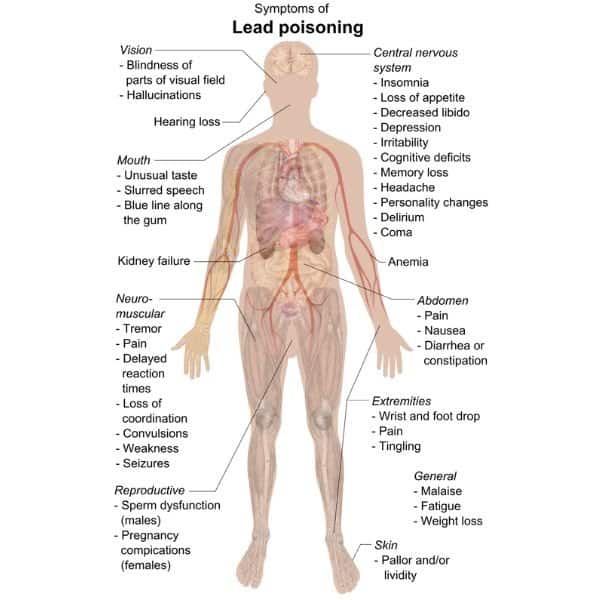
Health Effects of Lead Poisoning
Lead poisoning is a real and serious health hazard that affects over half a million children worldwide. Lead is an element that naturally occurs in trace amounts in the environment, but high concentrations can cause serious damage to the body.
- It has been linked to physical and psychological impairments, with effects ranging from mild to severe.
- Lead exposure primarily occurs through ingestion or inhaling lead particles, which can enter the bloodstream and impact multiple organs throughout the body.
- In children, this can lead to slowed growth rates, behavioral issues, and learning disabilities due to cognitive impairment.
- Other health concerns include kidney damage, reproductive issues, hypertension, and anemia. Long-term exposure may also increase the risk for certain cancers, such as ovarian cancer, later in life.
Since lead is harmful even at low levels, the Environment Protection Agency (EPA) has set its maximum contaminant level (MCL) to zero in drinking water. It’s worth mentioning that lead can accumulate in your body over time.
EPA also set an action level of 15 parts per billion (ppb). This means if more than 10% of the samples have lead levels beyond 15 ppb, public water systems should take measures to reduce the amount of lead as this is not safe and healthy for the public.
Conclusion
Lead found in drinking water is a serious health threat that can have lasting effects on the development and functioning of the human body. Brita’s Elite filters and faucet filters are a great way to reduce the amount of lead in drinking water by removing sediment and absorbing certain contaminants, including lead. While this type of filter cannot remove all lead from drinking water, it can be a helpful tool for reducing exposure to lead.

