Basics Of Reverse Osmosis
Before we go in-depth on the different aspects of reverse osmosis and how it works to your benefit, you must understand its fundamentals.
Understanding Osmosis
Osmosis is the process involving the movement of a solvent through some selectively permeable membrane to reach a different side that is characterized by the presence of more solute.
Thanks to the osmosis process, the two sides become better balanced regarding how much solute they contain.
That balance is critical; our bodies’ cells need it to function to the best of their capabilities. It’s also worth noting that osmosis will continue until both sides have become balanced.
No energy is required for osmosis, and the process happens naturally.
The Differences Between Osmosis and Reverse Osmosis
The first significant dissimilarity between osmosis and reverse osmosis is the fact that the latter requires the introduction of an external force to be completed.
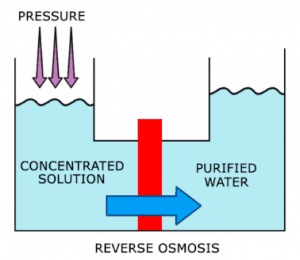
Instead of looking to achieve balance, reverse osmosis aims to separate the different components of the solution effectively. For the most part, that means separating the larger particles from the water they were previously floating in.
With the help of the external force, only clean water makes its way through a semi-permeable membrane to the other side while the larger contaminant particles are left in a different section.
The Reverse Osmosis Membrane
The reverse osmosis membrane uses a semi-permeable, thin-film composite with small holes that allow water to pass through but block larger particles.
The particle size of the small holes is in the range of 0.0001 to 0.001 micrometers which are 100,000 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair.
The membranes used in filtration systems can reach up to 40 inches long and have an effective surface area of 350-450 square feet.
They vary in diameter, with the main options being 2-inch, 4-inch, and 8-inch membranes.
How Does It Remove Contaminants?
The entire process is highly dependent on water pressure.
It pushes the unfiltered water through the semi-permeable membrane to separate the impurities from the clean water. Any undissolved solids will be removed via that process.
The impurities separated from the clean water will eventually be treated as waste and drained from the system. They will not be in contact with the clean water.
What Does Reverse Osmosis Remove?
All kinds of contaminants usually float around in the water that flows into our homes. Those contaminants are why drinking unfiltered tap water can be risky.
Here are some of the most notable contaminants removed by reverse osmosis filtration systems:
- Arsenic – Prolonged exposure to drinking water containing arsenic can lead to serious health issues such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
- Chlorine – Continuous consumption of chlorinated drinking water increases a person’s risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Fluoride – Elevated fluoride levels in the drinking water can cause teeth discoloration and skeletal fluorosis.
- Lead – Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) says that exposure to lead-contaminated drinking water can stunt children’s growth while also triggering behavior and learning issues. Pregnant women risk giving birth prematurely if they regularly drink lead-laced water. Healthy adults may also suffer from reproductive and cardiovascular problems if lead is in their drinking water.
- Mercury – Ingesting even minuscule amounts of mercury via your drinking water can have severe effects on your body. The main effects brought about by ingesting mercury are neurological and renal problems.
Is Reverse Osmosis Water Good For You?
Although some controversial statements surround the acidity and lack of minerals of reverse osmosis water, WQA debunked the danger of consuming purified water.
Furthermore, some systems will have several post-filters which increase the pH level with natural alkaline minerals. It is safe to consume reverse osmosis water.
While most of the contaminants will not immediately impact our bodies, impurities such as Mercury will accumulate and eventually hurt the neural system.
Drinking reverse osmosis water will remove 95-99% of water-borne contaminants.
Reverse osmosis improves the qualities of the water in its taste and odor. It encouraged me to drink more water and stay hydrated. Clean water will enhance the flavoring of beverages such as coffee and tea.
How Does A Reverse Osmosis System Works?
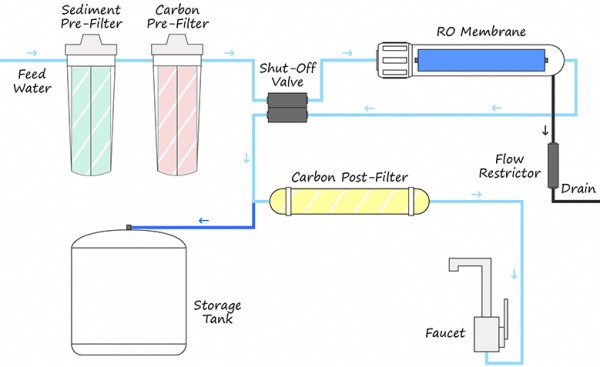
A reverse osmosis system will have these four primary stages to produce purified water.
- 1st Stage: Pre-Filtration
- 2nd Stage: RO Membrane Filtration
- 3rd Stage: Storage
- 4th Stage: Post Filtration
Below is a detailed explanation of all stages and why they are crucial for the system.
1st Stage: Pre-Filtration
Although the semi-permeable membranes can filter the vast majority of water-borne contaminants, they can get clogged up easily with larger particles.
Sending the unfiltered water directly through the membrane will essentially shorten its lifespan.
A pre-filter usually consists of carbon and sediment filters responsible for removing the largest particles in the water in preparation for the membrane to remove whatever remains in the water.
Installing some water softener at home can make things even easier on the system.
2nd Stage: RO Membrane Filtration
With the larger particles filtered out, the water can now be pushed through the membrane with water pressure.
The membrane removes microscopic contaminants such as lead, arsenic, and dissolved solids, thus making the water suitable for human consumption.
3rd Stage: Storage
The multi-stage filtration process will take a while to generate clean water. Hence, most of the system will funnel the filtered water directly into the storage tank. The storage tank ranges in size between 3.2 to 4 gallons.
4th Stage: Post-Filtration
In the unlikely event whereby contaminants pass through the membrane, a carbon filter will act as a final protective layer that removes any remaining impurities before the water is directed out via the faucet.
Old tubes and storage tanks sometimes contribute to bad odors and foul taste of the filtered water. This is where the post-carbon filter comes in and removes it, leaving behind only clean water.
Benefits And Drawbacks
As with any product you consider adding to your home, some pros and cons come with using a reverse osmosis filtration system.
Let’s dissect those benefits and drawbacks here.
Benefits:
- Effectiveness – A reverse osmosis filtration system can remove 95 to 99 percent of contaminants in the water supply with a semi-permeable membrane.
- Convenience – Unlike other water filters, a reverse osmosis system has a pre-filter that works on dirty water. The water doesn’t have to be at a certain level of cleanliness beforehand.
- Energy-efficient – No energy is required when using a reverse osmosis system.
- Great Separation – Contaminants are removed by reverse osmosis, kept separate from the clean water, and eventually drained from the system.
- High-capacity – Filters in reverse osmosis systems can last for 6 to 12 months before they have to be replaced. The reverse osmosis membrane could last up to 3 years.
Drawbacks:
- Costly investment – In the long run, you can save money using a reverse osmosis filtration system, but you will have to spend a significant amount upfront to add it to your home.
- Clogging – The reverse osmosis membrane will easily clog if the pre-filters are not working well.
- Slow Flow Rate – It’s best to have your filtration systems running well before you need the water. They take quite a bit of time to produce clean water.
- Waste Water – Some systems can produce as high as 3 gallons of wastewater to get 1 gallon of filtered water. However, the water could be channeled for other use such as gardening and washing.
- More Acidic Water – The lack of minerals makes the water acidic. However, the effect can be negated once it made contact with our saliva.
Maintenance For Reverse Osmosis System
The entire system generally lasts 10 to 15 years before falling apart.
However, regular replacements are needed for individual filters as they are routinely exposed to contaminants.
Pre-Filter: 6-12 Months
Pre-filters are often the ones that degrade the fastest, as they are the first to be exposed to contaminated water.
Although the lifespan varies between systems, generally, they can last for at least six months to a year before replacement.
It is generally a good idea to replace the filter in 12 months to avoid clogging that happens at a later stage.
Semi-Permeable Membrane: 2 – 3 Years
The semi-permeable membrane that is prominently involved in reverse osmosis also has to be replaced. The good news is that they last longer than the pre and post-filters.
Usually, the membranes will last between 2 to 3 years, depending on the usage and contamination levels.
You should also remember to have the whole filtration system professionally cleaned once every year to ensure it can work for a long time.
Post-Filter: 12 Months
The post-filters used in systems have longer lifespans than pre-filters, which is unsurprising given that they have fewer contaminants.
Check up on them every 12 months to see if they need to be replaced.
The Uses Of Reverse Osmosis
Besides residential, reverse osmosis is widely used in industrial sectors such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceutical production, seawater desalination, and many more.
The technology has been deployed for over a century and commercialized since the 1960s.
In many countries, reverse homeowners and even campers mainly use osmosis filtration systems to secure a relatively small clean water supply. The water coming from the system may be enough for a small family’s level of consumption.

More than 100 countries rely more on reverse osmosis systems because they need to turn saline water into water that people can use through a process known as desalination.
Countries heavily using reverse osmosis plants include Saudi Arabia, Singapore, and Kuwait.
Wrap Up
Reverse osmosis filtration systems exemplify how human ingenuity has helped improve everyday life. By taking a cue from the natural process known as osmosis, we can now produce cleaner and safer water for everyone to consume.
If you want a steady supply of clean water, check out one of our latest guides on the best reverse osmosis water system.
